As we have described before how to find XPath in the browser, here we are going to describe different dynamic XPath functions.
What Is Dynamic XPath In Selenium?
XPath, or XML Path, is one of Selenium WebDriver’s most commonly used locators for navigating a page’s HTML structure. It can locate any element in a web page using HTML DOM structure in HTML and XML documents.
XPath allows XML document navigation to select individual elements, attributes, or other parts of an XML document for specific processing. For example, XPath generates reliable locators but is slower in terms of performance than CSS Selector.
The language XPath is used to select elements in an HTML page. Using XPath, you can find any element on a page based on its tag name, ID, CSS class, etc. In Selenium, there are two types of XPath. Dynamic XPath is also called as custom XPath and it is one way to locate element uniquely.
Dynamic XPath is used to locate exact attribute or decrease the number of matching nodes/result from a webpage and following XPath expressions can be used for the same:
- Contains
- Sibling
- Ancestor
How to find XPath for dynamic elements in selenium?
XPath axes from the current node are utilized to locate dynamic elements in Selenium, allowing the search for nodes in the XML document. This is crucial for finding nodes closest to the tree. XPath axes provide methods for locating dynamic elements that standard XPath methods might miss, especially when identifiers like ID, Classname, or Name are absent.
In Selenium WebDriver, axes methods such as child, parent, ancestor, sibling, preceding, self, etc., are commonly employed to handle dynamically changing elements.
Modifying test scripts due to changes in the Application Under Test (AUT) is a challenging task in automation testing. Developers frequently alter identifiers, and elements may dynamically change during execution.
Automation testers should avoid setting fixed XPaths for test case elements to overcome these challenges. Instead, they should dynamically script XPaths based on specific patterns, ensuring adaptability to changes in the AUT.

Optimize Test Scripts: Improve your Selenium WebDriver scripts with dynamic XPath!

Pooja Upadhyay
Director Of People Operations & Client Relations
Contains
Contains is used to locate the web element who matches the specific text from multiple blocks.
As per the below image, if in your web page, there are sections that have the same element for all row, then you can find the specific element by using Contains to select text in that row.
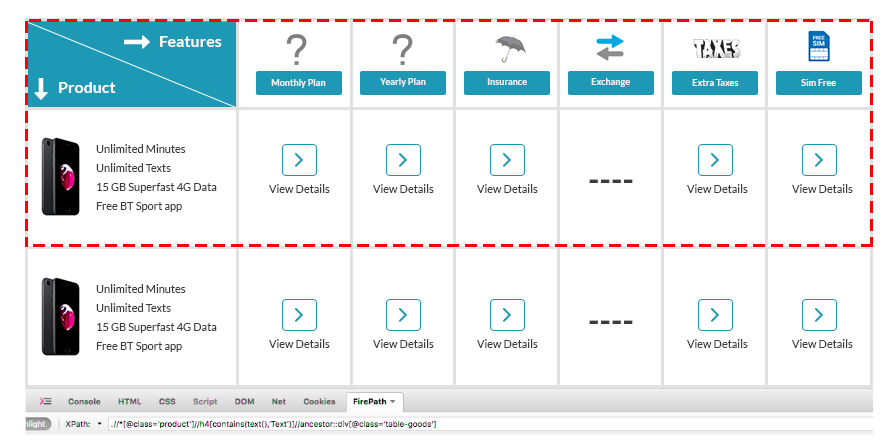
Example: .//*[@class='product']//h4[contains(text(),'Text')]//ancestor::div[@class='table-good'] .//*[@class='product']//h4[contains(.,'Text')]//ancestor::div[@class='table-good']Sibling
As the meaning of sibling, we can use this to find an element which is related to some other element. There are basically two types of sibling function which are used in XPath.
A) Preceding Sibling – If we select one sibling from given list, the “preceding sibling” function takes the preceding options of the selected one.
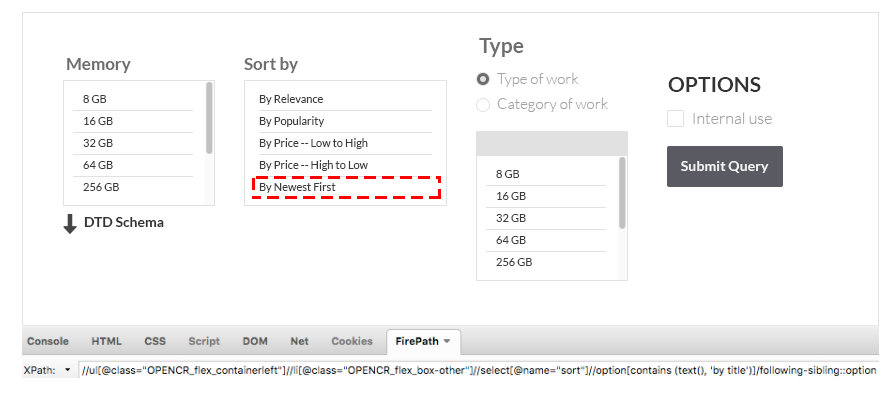
Example:
//ul[@class="OPENCR_flex_containerleft"]//li[@class="OPENCR_flex_box-other"]//select[@name="sort"]//option[contains (text(), 'by title')]/preceding-sibling::optionB) Following Siblings – If we select one sibling from given list, the “following sibling” function takes the following options of selected one. Example:
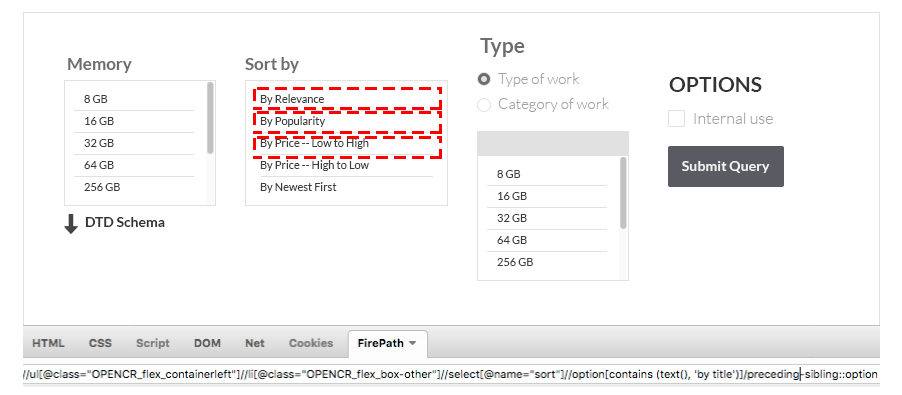
//ul[@class="OPENCR_flex_containerleft"]//li[@class="OPENCR_flex_box-other"]//select[@name="sort"]//option[contains (text(), 'by title')]/following-sibling::optionAncestor
We can use this to find an element on basis of the parent element. As per below image, if in your web page there is a section which has a same element for all the rows then you can find one row element by using ancestor.
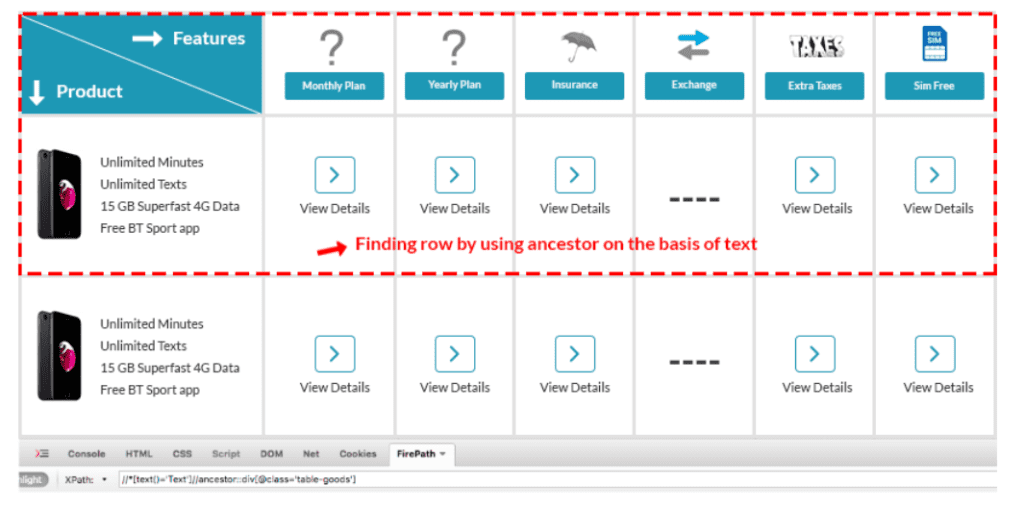
Why Upgrade to TYPO3 v13.0?
Upgrading to the latest version of a CMS can sometimes be a daunting decision. However, the benefits of TYPO3 v13.0 make a compelling case for the transition.
Staying Current with Technology
Upgrading ensures your website stays current with the latest web technologies and best practices. This benefits the user experience and helps maintain a modern and secure digital presence.
Leveraging New Features for Competitive Advantage
The features and enhancements in TYPO3 v13.0 provide a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to leverage powerful digital marketing tools and web development capabilities that can drive growth and success.
Ensuring Long-term Support
Staying up-to-date with the latest version of TYPO3 ensures that you will continue receiving updates and community support. Over time, this is vital for maintaining a secure and functional website.
Preparing for TYPO3 v13.0
Before upgrading to TYPO3 v13.0, preparing for the transition is essential.
Assessing Your Current Setup
Evaluate your current TYPO3 setup, including custom extensions and integrations. Ensure they are compatible with the new version or plan for necessary updates.
Planning for Content Migration
If migrating content, plan carefully to ensure that no data is lost and that SEO rankings are preserved.
Training and Support
Consider the training your team needs to adapt to TYPO3 v13.0’s new features and interface. Providing the necessary support will facilitate a smooth transition.
Conclusion
TYPO3 v13.0 is a significant leap forward for the CMS, offering a wealth of features and enhancements that cater to the needs of digital marketers, web developers, and content editors. Upgrading to TYPO3 v13.0 can enhance your user experience, streamline your web development processes, and empower your digital marketing strategies with advanced tools. As the digital landscape evolves, staying ahead with TYPO3 v13.0 could be the key to unlocking tremendous online success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still, have some queries? Find answers below
Selenium handles dynamic links using techniques such as relative XPaths or unique attributes. These methods ensure flexibility in identifying links even when the webpage structure changes.
Selenium checks dropdown values by navigating to the webpage, locating the dropdown element, and verifying its enabling, visibility, and ability to allow multiple selections.
To get all links on a webpage, Selenium navigates to the desired page, retrieves a list of ‘a’ tag elements, and iterates through the list, printing link text and addresses.
Handling dynamic dropdowns involves actions like triggering dropdowns by typing, selecting options, and adapting to changes in the dropdown menu dynamically.
Dynamic web elements are identified using techniques like XPath with ‘contains’ or ‘starts-with,’ allowing flexibility in locating elements that may change the structure.
XPath is a powerful web locator in Selenium used to navigate XML documents and locate elements based on various attributes like tag name, ID, or class.
Apart from XPath, Selenium uses various locators like ID, Name, Class Name, Tag Name, Link Text, and Partial Link Text to identify and interact with WebElements.
Absolute XPath begins from the root, while Relative XPath starts from the current node. Relative XPath is preferred for flexibility and adaptability to changes in the webpage structure.
XPath is versatile and can be dynamically adapted to locate changing or dynamic WebElements using techniques like ‘contains,’ ‘starts-with,’ or other flexible approaches.

Dive deep into the world of dynamic XPath to precisely locate elements for Selenium automation.

Pooja Upadhyay
Director Of People Operations & Client Relations

