For understanding testing approaches of IoT, we first need to understand what is IoT.
What is IoT?
IoT or Internet of Things was coined by Kevin Ashton, the co-founder of Auto-Id Center in the year 1999. It was introduced to remove the gap between physical and digital world.
IoT is a connection of various home appliances, industrial devices, vehicles, medicinal equipment, sensors, smoke detectors, etc., and operated remotely. All devices will be interconnected to each other at the certain location and operated remotely using the portable device like mobile phones or laptop from other location !!
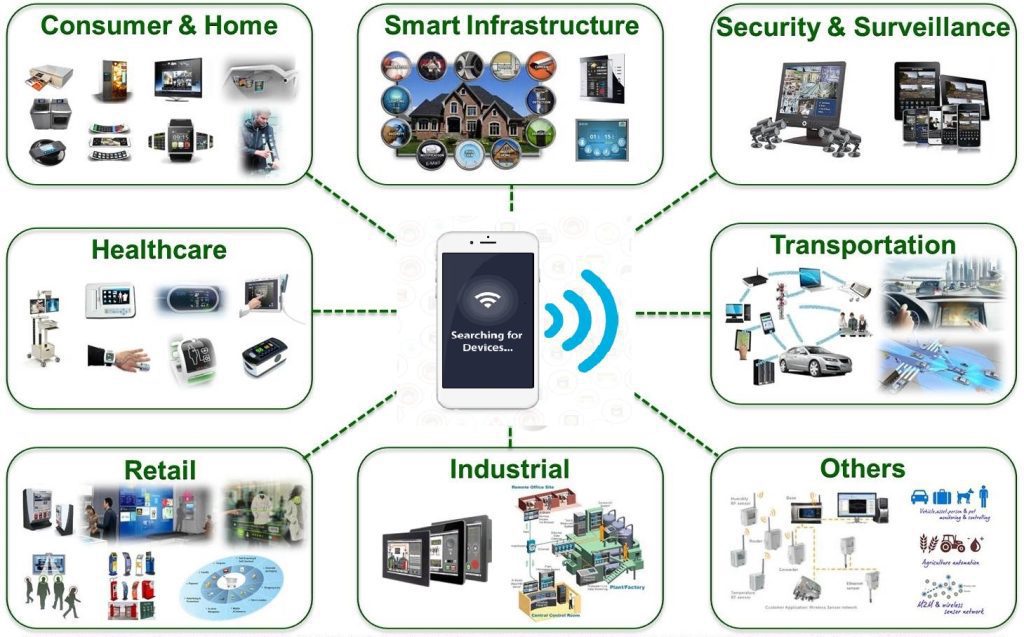
IoT real-world scenarios
- Your alarm rings everyday at 7 O’clock to wake you up so that you can reach at the office on time. Suppose you take 20 minutes to reach office from your home on normal days, but imagine that today is a rainy day so you will drive slow compared to other day and reach in 30 minutes. Based on weather forecast data, an alarm should automatically set to 6:50 am so that you can reach office on time. Similarly, if your coffee maker is connected with that system, then it will make coffee accordingly !!

- Smart Home system is the highly typical and complicated project of IoT. It is a dream to connect all home appliances and enable them to send and receive data over the network, though some companies have made that dream come alive. Certain research data shows that around 256 companies and startups are involved in IoT Smart Home projects. The total amount of funding for Smart Home startups currently exceeds $2.5 billion(approximately). This list includes some popular names such as Nest or AlertMe, Philips, Haier, Belkin, etc.
Technologies used in IoT
The most interesting question comes here that “How these devices will be connected?”. Some of the most common technologies used in IoT implementation are:
- Bluetooth: IoT Device can connect using Bluetooth. Bluetooth can establish the connection between devices to enable communication and exchange data.
- WiFi(Wireless Fidelity): WiFi creates a wireless network which helps in sending and receiving data packets to enable communication between IoT devices.
- Z-Wave: Z-Wave is a wireless network standard that consumes very low power and it is widely used for connecting smart devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) like home automation, security markets, etc. Z-Wave is a complete communications solution, which consists of everything from the physical layer to the applications layer.
- RFID(Radio Frequency Identification Code): RFID used to track consumer product worldwide. RFID is an intelligent barcode that can be operated using the networked system to track the product, vehicles or any object.
IoT testing approaches
If anything is developed then it is compulsory to test it. So there are various testing approaches for IoT. Some of them are:
IoT Security
In IoT, devices are equipped with IP Addresses and has the ability to transmit data over the network. When network comes into picture then security should be the first priority. From a testing standpoint, we need to check if the data is encrypted when getting transferred from one device to the other. In case of UI, set password protection in ON mode.
Usability
There should be assured that all devices connected in the network are always available as well as performing well. Also, there should be an option to maintain a log of all devices to monitor individual’s functionality and behaviour.
Connectivity
In case of IoT, connectivity is a must. Communication between the device and its operator will only be established if there is connectivity between them. Testing under connectivity includes two possibilities
Testing of data that is transmitted over the network when connected in a network.
There is a possibility of a system to go offline definitely once. So it becomes important to check the behaviour of the system during offline period.
Pilot testing
Pilot testing is also one of the important testing processes in IoT implementation. Pilot testing is verifying the entire system or a single component under real-world operating conditions, or we can say its a rehearsal for the usability of a system.
IoT software testing tools
In IoT, there are various tools for testing both hardware and software individually. Some of the software testing tools are :
Wireshark
Wireshark is an open source and free network traffic analyzing software. It is used to monitor all the traffic visible on that interface including unicast traffic. It is similar to tcpdump but has a GUI(Graphical User Interface), also it has some sorting and filtering options. It’s another version without GUI is known as TShark. It runs on Linux, macOS, BSD, Solaris, some other Unix-like operating systems, and Microsoft Windows.
Tcpdump
Tcpdump does similar jobs as that of Wireshark but it doesn’t have GUI. It is a command line utility that displays sent and received TCP/IP and other packets over the network.
I hope this blog helps you to expand your IOTr knowledge…! If you need more assistance for IoT App Development feel free to connect with us. Thanks!
Frequently Asked Questions
Challenges include interoperability between devices, security concerns, diverse communication protocols, and the sheer scale of interconnected devices, making testing complex.
IoT testing tools assess vulnerabilities in devices, networks, and data transmission, helping identify and fix potential security issues before they can be exploited.
Performance testing assesses how well IoT devices handle different loads and scenarios. It helps identify bottlenecks and ensures devices operate optimally under various conditions.
IoT testing tools simulate large-scale deployments to evaluate how devices handle increased loads. This is essential to ensure that IoT solutions can scale seamlessly as the number of connected devices grows.
Yes, tools like OWASP IoT Project, Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP), and ThreatModeler focus on identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities in IoT devices and networks.
Automation is crucial for efficiently testing many scenarios and devices in IoT. Automated testing tools help save time, improve accuracy, and increase test coverage.
Comprehensive testing involves a mix of manual and automated testing, covering functional, security, performance, and compatibility aspects. Regularly updating testing strategies to adapt to evolving IoT landscapes is also essential.
