The World Wide Web (WWW or Web) is an information space in which documents and other web resources are identified by Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), interlinked by hypertext links, and accessible via the Internet. The Web is a global network of connected computers that communicate and share information through the Internet. In this article, we’ll explore what Web 3.0 is, how it works, and its potential implications for the future of the Internet.
The Current State of the Internet
Today, the Internet is dominated by centralized systems controlled by large corporations and government entities. This centralization has led to a need for more privacy, security, and control for Internet users. For example, personal data is often collected and sold to advertisers, while governments and corporations censor online content. Centralized systems are also vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and other security risks.
Evolution of Web
The evolution of the World Wide Web can be divided into several stages, including:
Web 1.0 (1993-2004): Characterized by static HTML pages and limited user interactivity.
Web 2.0 (2004-2009): Characterized by dynamic and user-generated content, social media, and increased collaboration and communication between users.
Web 3.0 (2010-present): Characterized by decentralized technology (e.g., blockchain), semantic web (structured data), and artificial intelligence. Web 3.0 emphasizes greater privacy, security, and user control over data.
Emerging technologies: Including the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and virtual/augmented reality, are expected to shape the future of the web.
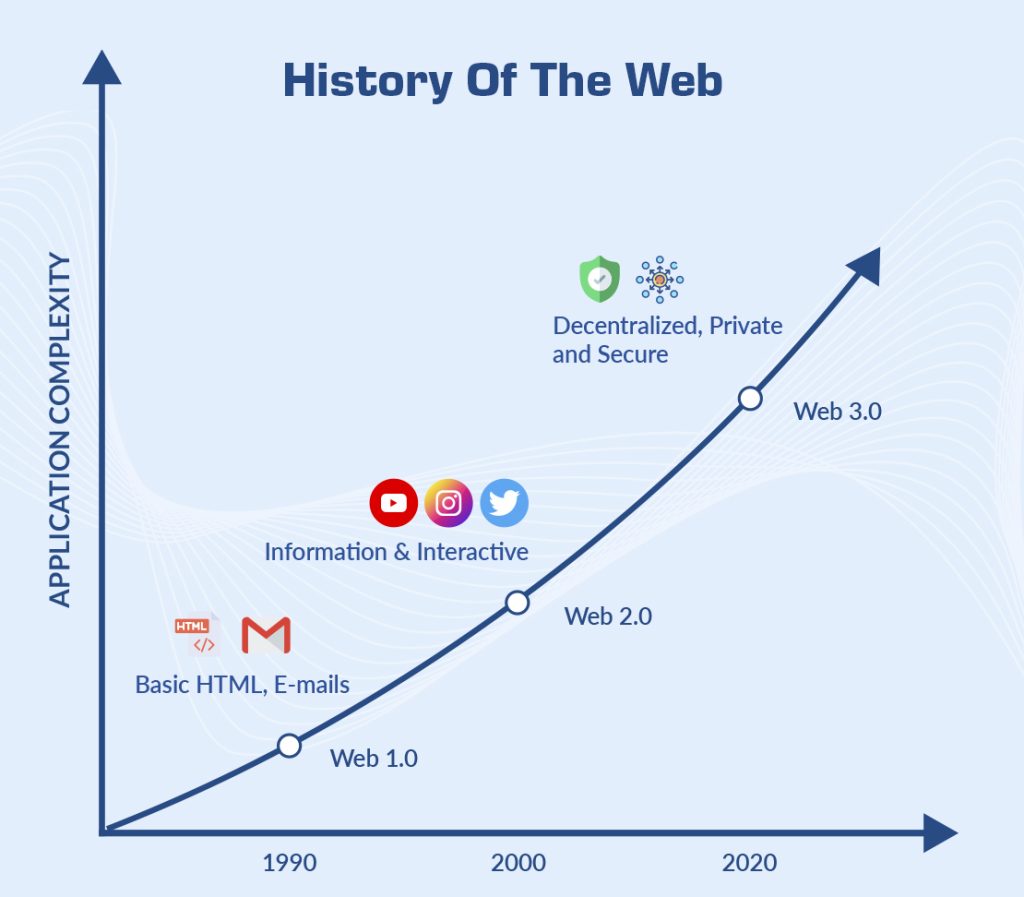
The evolution of the web has been driven by the increasing demand for more interactive, personalized, and connected online experiences and the need for greater security, privacy, and control over data.
Related Article: eCommerce & Metaverse What to Expect in the Future? Open configuration options
What is Web 1.0
Web 1.0 refers to the first generation of the World Wide Web, characterized by static HTML pages and limited user interactivity. It was primarily used for delivering information to users rather than enabling them to participate in creating and sharing content actively.
What is Web 2.0
Web 2.0 is the second generation of the World Wide Web, characterized by dynamic and user-generated content, social media, and increased collaboration and communication between users. It allows for greater interactivity and collaboration online and emphasizes the shift from a web of information to a web of participation.
What is Web 3.0
The next generation of the web is characterized by increased personalization and semantic understanding, enabled by technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Semantic Web. It aims to create a more intelligent and intuitive web where humans and machines can quickly process and understand information.
Web 3.0 and Decentralization
Web 3.0 aims to address these issues by leveraging blockchain technology to create a decentralized Internet. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores data securely and transparently. In a decentralized network, no central authority controls the data, as all nodes in the network have equal control and access to the data.
In Web 3.0, users own their data, and transactions and storage are managed through decentralized applications or dApps. Unlike centralized apps, dApps run on a decentralized network and are not controlled by any single entity. This means that users have complete control over their data, and there is no central point of failure that malicious actors can exploit.
Web 3.0 and the Future of Internet
Web 3.0 has the potential to change the way we use the Internet and interact with digital assets. Here are a few critical benefits of Web 3.0:
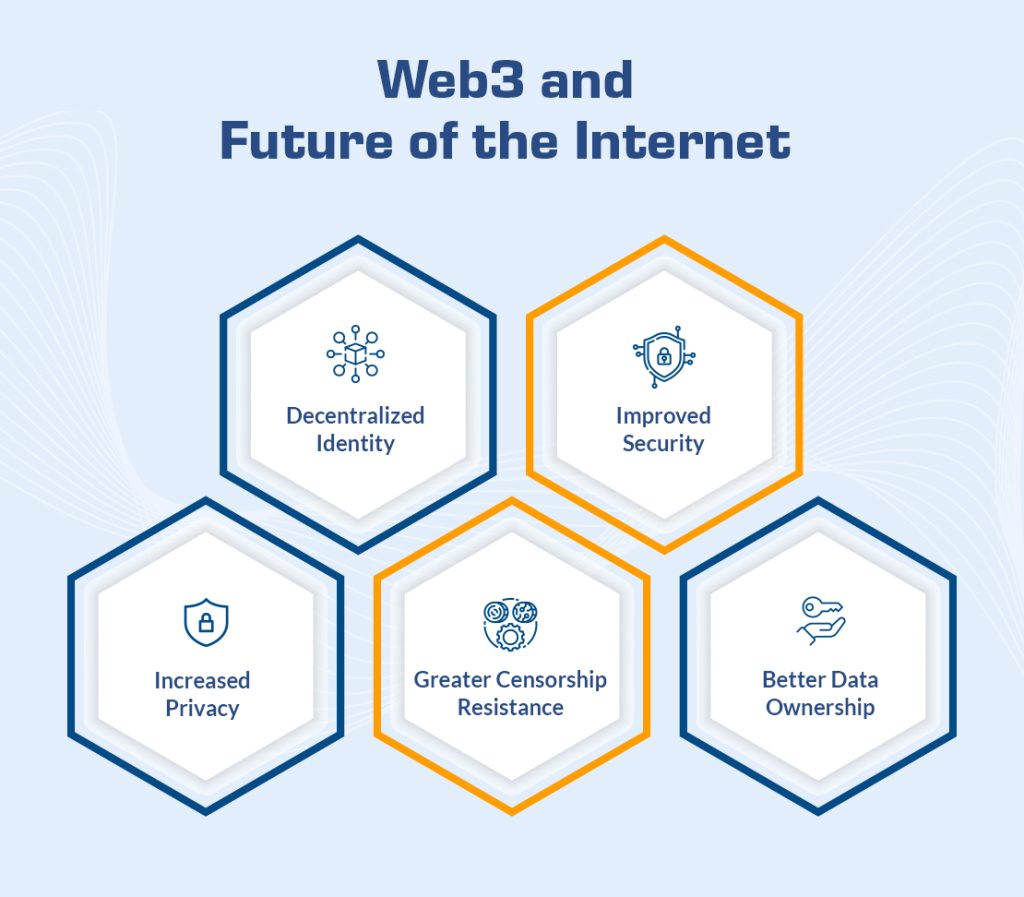
Decentralized Identity:
Web 3.0 allows users to control their digital identity, making it impossible for any central authority to control or manipulate their online data. This means that users can authenticate themselves on the Internet without relying on third-party authentication systems.
Improved Security:
Decentralization eliminates the central points of failure in centralized systems, making it much more difficult for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities. This results in a much more secure Internet, where users can be confident that their data is protected.
Increased Privacy:
Web 3.0 eliminates the need for users to trust third-party organizations with their personal data. This means that users can have more control over who has access to their personal information and how it is used.
Greater Censorship Resistance:
Any single entity does not control Web 3.0, making it much more difficult for governments and corporations to censor online content. This means that users can access and share information freely and without fear of censorship.
Better Data Ownership:
In Web 3.0, users own their data, which is stored in a decentralized network. This means that users can control how their data is used and even monetize their data by selling access to it.
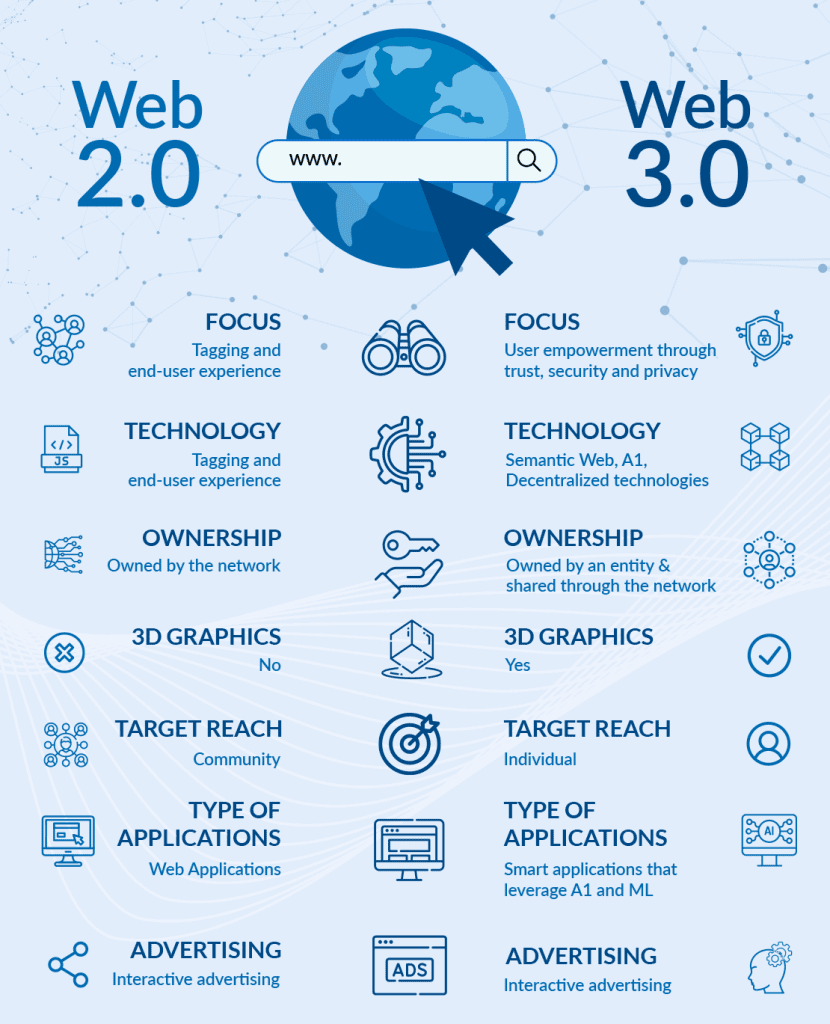
The Transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0
The transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 marks a significant shift in how the Internet is structured and how users interact with it. Web 2.0 was centered around user-generated content and social media, while Web 3.0 is focused on decentralization and empowering users with greater control over their data. Web 3.0 also incorporates artificial intelligence and structured data (the semantic web) to create a more intelligent and interconnected web. The transition to Web 3.0 is ongoing and driven by a growing desire for greater privacy, security, and control online.
Related Article: Everything You Need to Know About Metaverse
How to Build on Web 3.0
Building on Web 3.0 involves using decentralized technologies like blockchain, smart contracts, decentralized storage solutions, and new programming languages and development frameworks. Here are some steps to get started:
- Familiarize yourself with the basics of blockchain and decentralized technology.
- Choose a blockchain platform (e.g., Ethereum, Polkadot, etc.) and decide what type of decentralized application (dApp) you want to build
- Learn the programming language and development framework associated with your chosen platform (e.g., Solidity for Ethereum)
- Get hands-on experience by building a simple dApp or participating in hackathons and online communities.
- Test, deploy, and market your dApp on a decentralized app store or marketplace.
Note: Web 3.0 development can be complex and requires a solid understanding of blockchain technology and its associated protocols and a willingness to learn and experiment.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 represents a significant shift in how the Internet works, moving from a centralized system to a decentralized network. This decentralized network is more secure, private, and resistant to censorship, putting users in control of their digital assets and personal data. While Web 3.0 is still in its early stages, it has the potential to revolutionize the Internet and create a more secure and transparent online environment.
As the development of Web 3.0 continues, it will be exciting to see how this decentralized Internet of the future evolves and what impact it will have on the way we use and interact with the Internet. Whether you are an early adopter or a skeptic, it’s clear that Web 3.0 has the potential to.
Frequently Asked Questions
Web 3.0 is the next evolution of the internet that emphasizes decentralization, improved user experiences, and enhanced data security. It differs from Web 2.0 by placing more control in the hands of users and utilizing decentralized technologies like blockchain.
Decentralization in Web 3.0 means data is not stored on centralized servers but distributed across a network. This enhances security, reduces reliance on intermediaries, and gives users more control over their data and online interactions.
Web 3.0 is powered by technologies like blockchain, which ensures transparent and secure transactions without intermediaries. Smart contracts, decentralized storage, and identity management are also integral components of the Web 3.0 ecosystem.
Web 3.0 prioritizes user privacy by giving individuals greater control over their data. Decentralized identity solutions and encrypted communication protocols help protect personal information, reducing the risks associated with centralized data storage.
Yes, existing applications can transition to Web 3.0 by integrating decentralized technologies. Developers should consider data migration, interoperability, and user education when making this transition to ensure a smooth user experience.
Web 3.0 significantly impacts digital currencies, with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms utilizing blockchain to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions. This creates more inclusive and accessible financial services outside traditional banking systems.
Challenges include scalability, interoperability, and user education. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing technological advancements, collaboration within the development community, and efforts to raise awareness about the benefits of Web 3.0.
Web 3.0 allows content creators and users to own and control their digital assets through blockchain technology. Smart contracts enable transparent and fair monetization models, providing creators with direct compensation for their work.
Web 3.0 is designed to benefit both technical and non-technical users. While developers play a crucial role in building decentralized applications, non-technical users can experience the advantages of enhanced privacy, ownership of data, and new forms of digital interaction.
Individuals can start exploring Web 3.0 by familiarizing themselves with blockchain technology, decentralized applications (DApps), and related concepts. Resources include online courses, forums, and community events dedicated to educating users about the decentralized internet.
